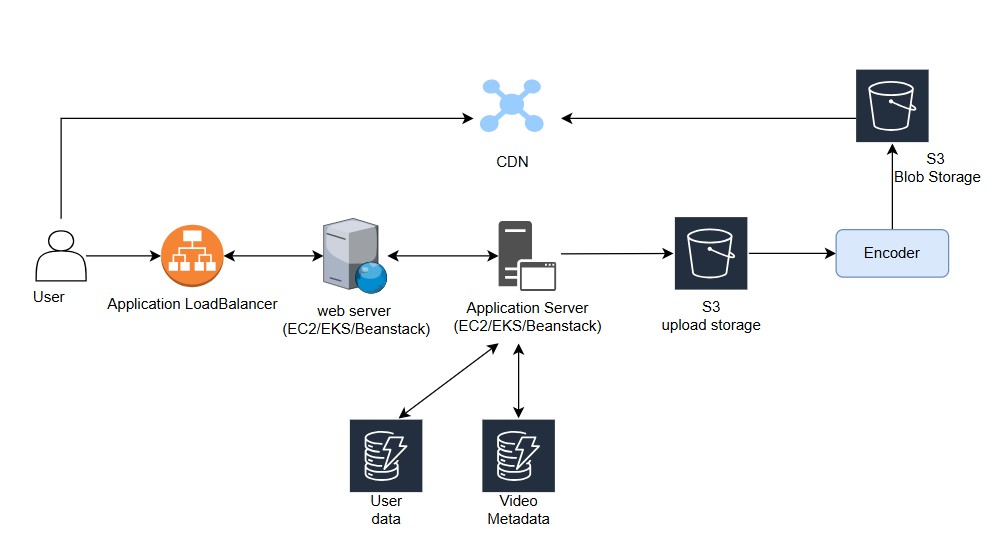
High Level Design - youtube
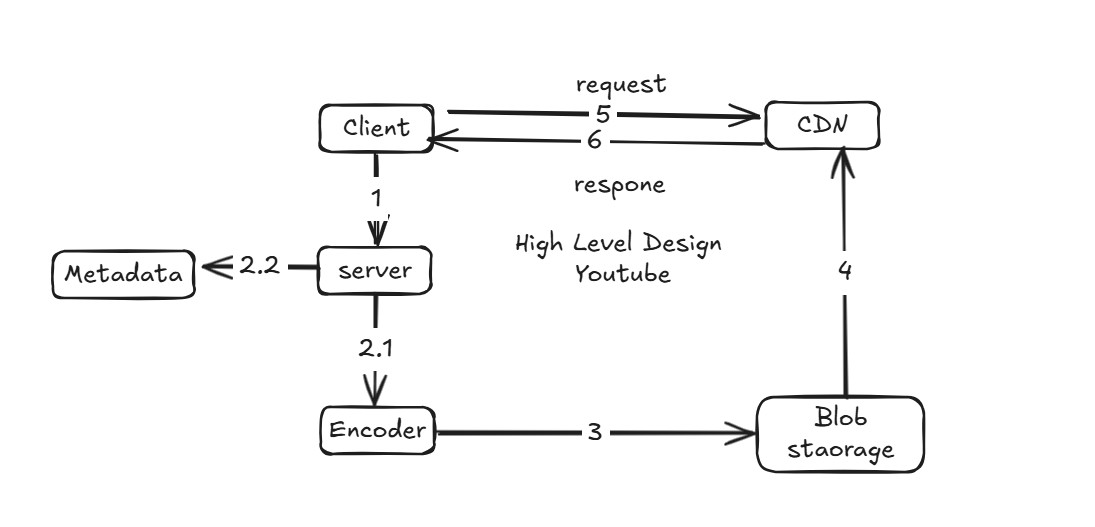
- Client uploads video → request goes to Application Server.
- Server sends raw video to Encoder for multi-format transcoding (240p–4K, HLS/DASH).
- Server extracts and stores metadata (title, tags, thumbnails) in Metadata DB.
- Encoded video chunks are stored in Blob/Object Storage (e.g., S3).
- Blob Storage pushes video chunks to CDN (e.g., CloudFront) for global caching.
- Client requests video from CDN edge location.
- CDN serves cached chunks directly or fetches from Blob Storage if not cached.